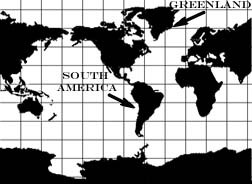
Figure 2.1.3, (“Miller Cylindrical,” USGS, 2006.
http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/MapProjections/projections.html)
|

Figure 2.1.3.1, (USGS, 2006.
http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/MapProjections/projections.html)
|
|
Description: Cylindrical projections are designed as if a cylinder
were wrapped around the world; both the longitude and latitude lines
are straight and parallel. The example above might fit nicely around
an empty paper towel roll. Notice that if a cylindrical projection
were wrapped around a globe it would not touch the poles at either
end unless it was crumpled up.
Advantages:
- can be created on a flat piece of paper, making it
convenient and inexpensive
- accurate for depicting small areas
- can depict the entire earth at once
Disadvantages:
- distorts large areas
- The areas near the poles appear larger than they really are.
For example, South America is eight times larger than
Greenland in reality, but on Figure 2.1.3 Greenland appears
to be larger.
|



